背景
- 加载或创建表、模型、Fileset 时,频繁访问数据库以获取
metalake_id、catalog_id、schema_id等元数据标识符,带来显著的性能开销; - casbin 在鉴权时需要根据 ID 进行权限判断,这需要频繁访问数据库获取 Entity 的 ID;
- Role 信息加载涉及大量元数据对象,也需频繁查询数据库,进一步加剧性能瓶颈;
- 引入缓存机制可显著降低数据库访问频率,从而提升整体访问性能。
目标
- 支持根据
NameIdentifier快速查找Entity; - 支持多种实现,包括本地内存缓存(如 Caffeine)与分布式缓存(如 Redis);
- 插件化设计,便于扩展;
- 同时支持
EntityStore、SupportsRelationOperations和SupportsTagOperations全部操作; - 不与底层 Storage 交互;
总体设计
EntityCache 的实现分为两个步骤:
- 为
EntityStore和SupportsRelationOperations的全部操作添加缓存; - 合并
SupportsTagOperations到SupportsRelationOperations;
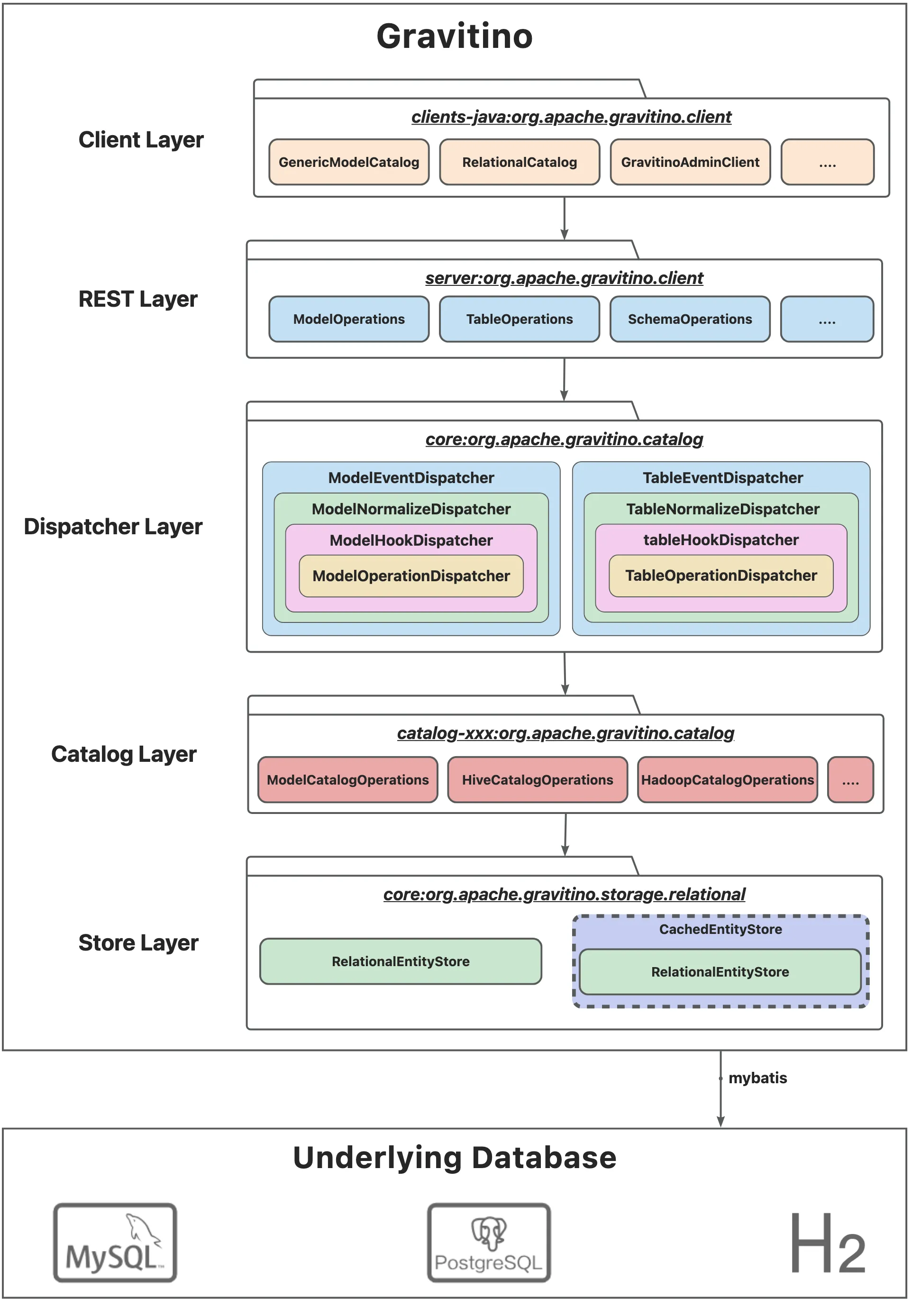
EntityCache 是 Store 层的缓存模块,采用插件化设计,可以支持本地内存缓存(如 Caffeine),也支持分布式缓存(如 Redis),主要用于加速元数据的读写操作。
设计分为两部分:
- Cache Data:用于存储
Entity本身; - Cache Index:用于辅助前缀查询。
缓存数据(Cache Data)
- 支持
NameIdentifier+EntityType→Entity的映射; - 支持
NameIdentifier+EntityType+RelationType→Entity列表的映射 - 缓存项支持可配置的过期策略,便于灵活控制缓存生命周期。
缓存索引(Cache Index)
- 支持基于名称前缀检索对应的 Entity 实体集合;
- 支持多种缓存过期策略,当 CacheData 中的缓存项因为策略过期被删除时,通过
remove listener保持 Cache Index 同步删除。
接口定义与实现
EntityCache
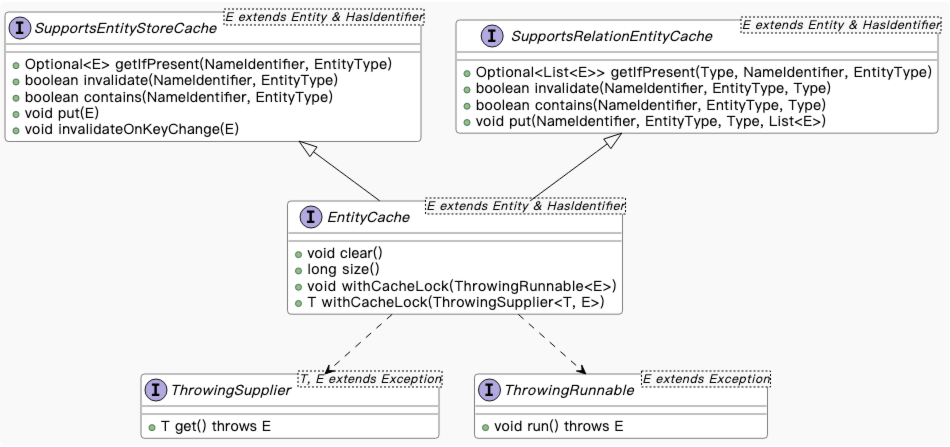
EntityCache 的接口类图设计如上,EntityCache 接口继承自 SupportsEntityStoreCache 和 SupportsRelationEntityCache 接口,这么设计的原因是为了区分适配的底层接口。
SupportsEntityStoreCache 接口用于包装 EntityStore 接口,负责 Entity 的底层操作,其具体代码如下:
public interface SupportsEntityStoreCache {
<E extends Entity & HasIdentifier> Optional<E> getIfPresent(
NameIdentifier ident, Entity.EntityType type);
boolean invalidate(NameIdentifier ident, Entity.EntityType type);
boolean contains(NameIdentifier ident, Entity.EntityType type);
<E extends Entity & HasIdentifier> void put(E entity);
<E extends Entity & HasIdentifier> void invalidateOnKeyChange(E entity);
}getIfPresent:缓存中读取(不触发加载);invalidate:显式清理缓存项;invalidateOnKeyChange:用于处理关联实体变更导致的联动清理。contains:检查特定键是否命中缓存;put:将一个 Entity 放入缓存;
SupportsRelationEntityCache 接口用于适配 SupportsRelationOperations 接口的操作,其具体定义如下:
public interface SupportsRelationEntityCache {
<E extends Entity & HasIdentifier> Optional<List<E>> getIfPresent(
SupportsRelationOperations.Type relType,
NameIdentifier nameIdentifier,
Entity.EntityType identType);
boolean invalidate(
NameIdentifier ident, Entity.EntityType type, SupportsRelationOperations.Type relType);
boolean contains(
NameIdentifier ident, Entity.EntityType type, SupportsRelationOperations.Type relType);
<E extends Entity & HasIdentifier> void put(
NameIdentifier ident,
Entity.EntityType type,
SupportsRelationOperations.Type relType,
List<E> entities);
}该接口定义的方法同 SupportsEntityStoreCache 接口,唯一的区别在于参数列表多一个 SupportsRelationOperations.Type。
EntityCache 的具体代码如下:
public interface EntityCache extends SupportsEntityStoreCache, SupportsRelationEntityCache {
void clear();
long size();
<E extends Exception> void withCacheLock(ThrowingRunnable<E> action) throws E;
<T, E extends Exception> T withCacheLock(ThrowingSupplier<T, E> action) throws E;
@FunctionalInterface
interface ThrowingSupplier<T, E extends Exception> {
T get() throws E;
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface ThrowingRunnable<E extends Exception> {
void run() throws E;
}
}clear:清空缓存中的所有条目;size:返回当前缓存中的条目数量;withCacheLock:在加锁的上下文中执行用户自定义逻辑,确保操作的线程安全;
在 EntityCache 中引入 withCacheLock 的主要目的是为了提供一个加锁的操作环境,以保证缓存整体操作的原子性和一致性。
缓存内部包含两个核心组件:
CacheIndex:用于前缀或关联索引检索;CacheData:用于实际的数据存储。
Cache 作为一个整体需要通过锁保证内部 CacheIndex 和 CacheData 两个部分的一致性。在执行涉及多个步骤的复合操作(如更新、清理、加载)时,需要保证这两个部分的数据在任意时刻保持一致,否则可能出现缓存脏读或状态不一致的问题。
尤其在 Store 层 的典型操作场景中,如 update 操作,通常包括以下流程:
- 清理缓存(防止旧数据被访问);
- 更新底层存储系统(如数据库或 Catalog);
- 将更新后的实体重新放入缓存。
为了保证这三个步骤作为一个整体执行时不会被其他线程打断,必须在整个流程上加锁,而不能仅依赖 put、invalidate 等单个方法内部的锁控制。
因此,withCacheLock 提供了一种显式的加锁机制,使得调用方可以在一个加锁的上下文中自定义一组操作,确保它们具备原子性和线程安全性。
ThrowingSupplier 接口是对标准 Java Supplier<T> 的扩展,支持在 get() 方法中抛出受检异常(checked exception)。其设计目的是用于在带返回值的延迟执行逻辑中,允许调用方在执行过程中处理和传播异常。这使得在 Lambda 表达式中处理数据库或 IO 操作等异常源时,更灵活,同时提升了 withCacheLock 方法的通用性和表达能力。
ThrowingRunnable 接口是对标准 Java Runnable 的扩展,支持在 run() 方法中抛出受检异常。它主要用于执行无返回值但可能抛出异常的操作逻辑。其设计逻辑同 ThrowingSupplier。
这两个接口作为 EntityCache 的加锁执行接口参数,提供了对缓存操作原子性保护的同时,也允许业务逻辑自由处理受检异常。
键值设计
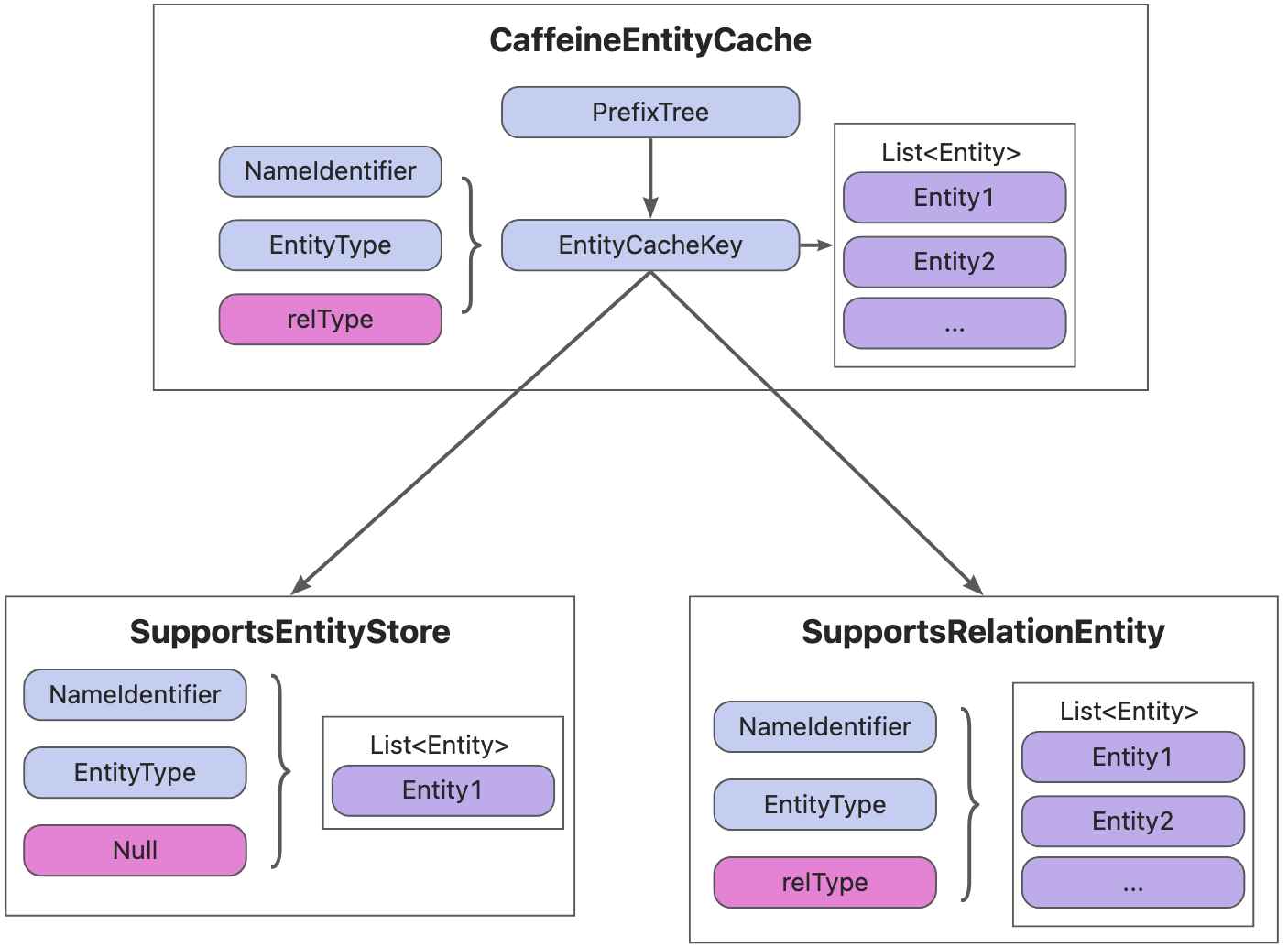
EntityCacheKey
EntityCacheKey 是缓存中用于唯一标识实体或实体关系的键对象,其设计来源于对 EntityCache 接口中两类操作的抽象:
对于 SupportsEntityStoreCache 接口,可以如下方式映射唯一的 Entity 对象:
NameIdentifier + Entity.EntityType对于 SupportsRelationEntityCache 接口,可以如下方式映射唯一的一组 Entity 对象:
NameIdentifier + Entity.EntityType + SupportsRelationOperations.Type因此,EntityCacheKey 包含以下三个核心字段:
NameIdentifier identifier:实体的命名标识;Entity.EntityType type:实体的类型;SupportsRelationOperations.Type relationType:关系类型(可选,用于关系缓存)。
EntityCacheKey 的 toString() 方法定义如下:
@Override
public String toString() {
String stringExpr = identifier.toString() + ":" + type.getShortName();
if (relationType != null) {
stringExpr += ":" + relationType.name();
}
return stringExpr;
}实现采用 identifier 作为字符串前缀,并追加类型与关系信息,从而保证键的唯一性和可读性。同时具备良好的前缀结构,有利于基于前缀的索引与检索操作(如在 ConcurrentRadixTree 中进行快速范围查询)。
EntityCacheValue
根据上述设计,缓存中的 Value 可以被统一抽象为一组 Entity 实例(List<Entity>),且每组至少包含一个元素。无论是单个实体缓存(如 Catalog、Table),还是关系型缓存(如 Role → Users 的映射),都可统一表示为一组相关联的 Entity 对象。这种抽象方式简化了缓存结构的处理,便于在内部统一管理、清理和加载缓存项。
Cache 实现
BaseEntityCache
BaseEntityCache 是一个抽象基类,用于实现 EntityCache 接口的通用逻辑。它主要负责一些缓存通用逻辑的封装和工具方法,并将核心的缓存驱逐实现(如 invalidateExpiredItem)留给子类完成。
public abstract class BaseEntityCache implements EntityCache {
protected final Config cacheConfig;
}核心字段是 cacheConfig 保存缓存的配置参数,并通过构造函数注入,确保不会为 null(使用 Preconditions 校验)。
除此之外,BaseEntityCache 还提供了多个静态工具方法供子类复用
getIdentFromEntity (Entity entity):安全地从 Entity 类型获取其 NameIdentifier;validateEntityHasIdentifier (Entity entity):校验Entity是否实现了HasIdentifier接口;convertEntities (List<Entity> entities):将原始Entity列表安全转换为指定泛型类型的实体列表;convertEntity (Entity entity):与上面方法类似,针对单个实体进行泛型转换。
此外,BaseEntityCache 还提供了 invalidateExpiredItem (EntityCacheKey key) 方法,该方法用于异步驱逐或过期清理逻辑。
CaffeineEntityCache
CaffeineEntityCache 实现类采用 Caffeine 实现。下面是 CacheData 和 CacheIndex 的示意图:
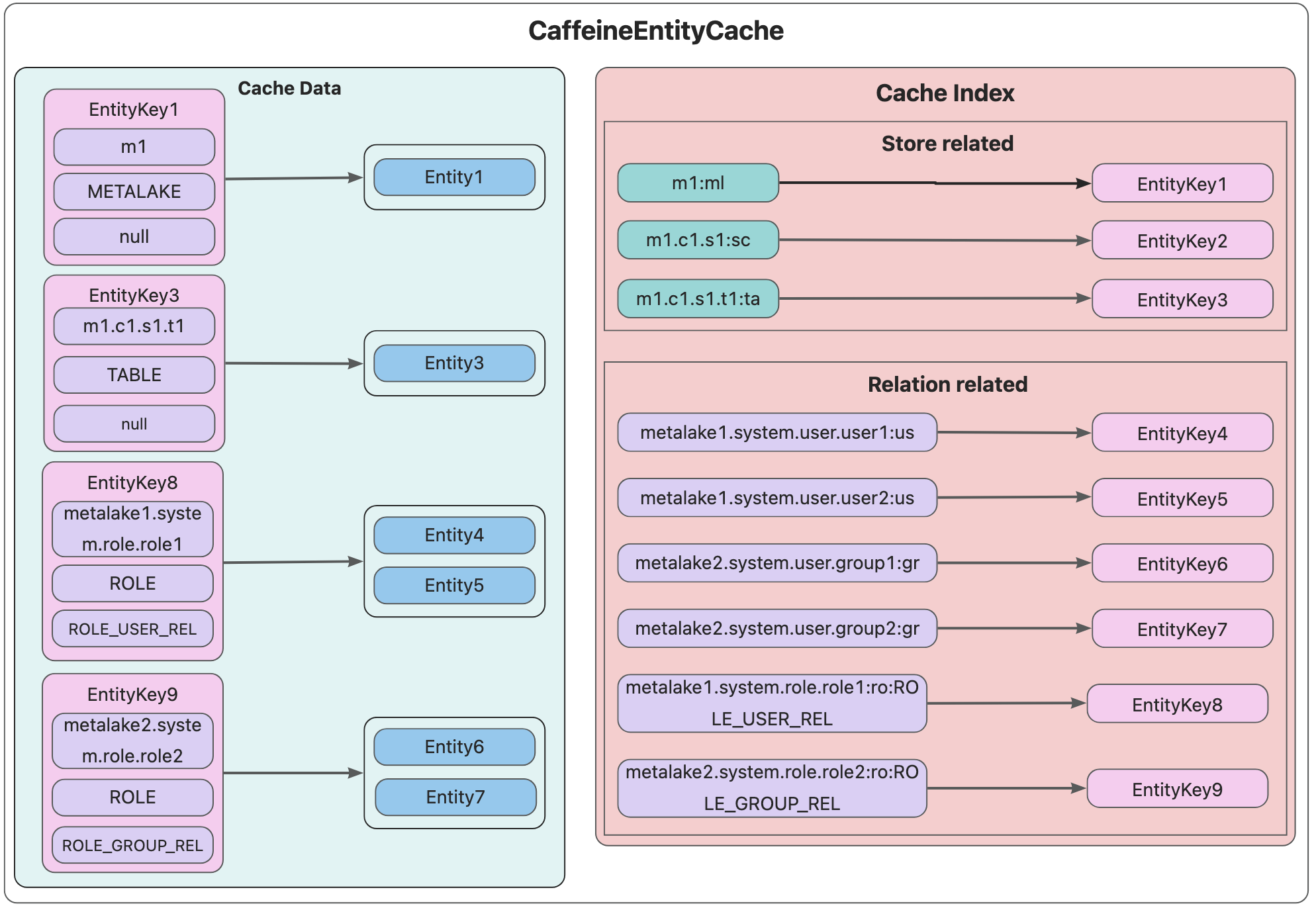
- CacheData:
EntityCacheKey→List<Entity> - CacheIndex:PrefixTree<String, EntityKey>
索引结构选型
ConcurrentRadixTree(来自 concurrent-trees)
- 线程安全,支持前缀查询、模糊匹配、高性能读写。
- 读取无锁,更新以 patch 方式应用,避免不一致状态。
- 使用节点级锁代替全树锁,提高并发写入能力。
- 空间效率高,采用路径压缩减少节点数量,提升缓存局部性。
PatriciaTrie(来自 commons-collections)
- 非线程安全,写入需锁全树,影响读写性能。
- 并发场景下易成为瓶颈。
与 PatriciaTrie 相比,ConcurrentRadixTree 具有以下关键优势:
- 无锁/读写分离:
ConcurrentRadixTree在读操作方面实现了 “近乎无锁” 的特性。读线程无需竞争锁,就能安全地遍历树结构。对于写操作,它会将更改内容打包成一个 “补丁”(patch),并以原子方式进行应用。这确保了读者要么看到补丁应用前的旧版本,要么看到补丁应用后的新版本,始终能获得一致的数据视图。这种设计在高并发场景下,能够显著减少读写冲突,有效降低操作延迟。 - 细粒度并发控制:
ConcurrentRadixTree内部采用分段或节点级别的锁来控制写入操作,避免了像使用synchronized对整个表加锁那样导致所有操作被阻塞的情况。在进行写入操作时,仅对受影响的子树或节点加锁,而其他分支仍可同时进行读写操作,从而提高了并发性能。 - 原生前缀/通配符查询:
ConcurrentRadixTree支持多种高效的查询方式,包括前缀查找、精确查找,还具备关键词扫描功能(ConcurrentInvertedRadixTree)。这些查询操作的时间复杂度为 ,m 为查询长度,借助路径压缩后的树结构,在查询过程中访问的节点数量更少,查询速度可与哈希表相媲美。 - 内存紧凑+快速路径压缩:相较于普通的 Trie 树,Radix Tree 能够将只有一个子节点的链路进行合并,从而减少树的深度和节点数量。这种优化不仅提高了内存利用率,还提升了缓存命中率,使数据访问更加高效。
get 操作
get 操作比较简单,如果命中缓存则返回 Optional<T> 否则返回 Optional. EMPTY;
put 操作
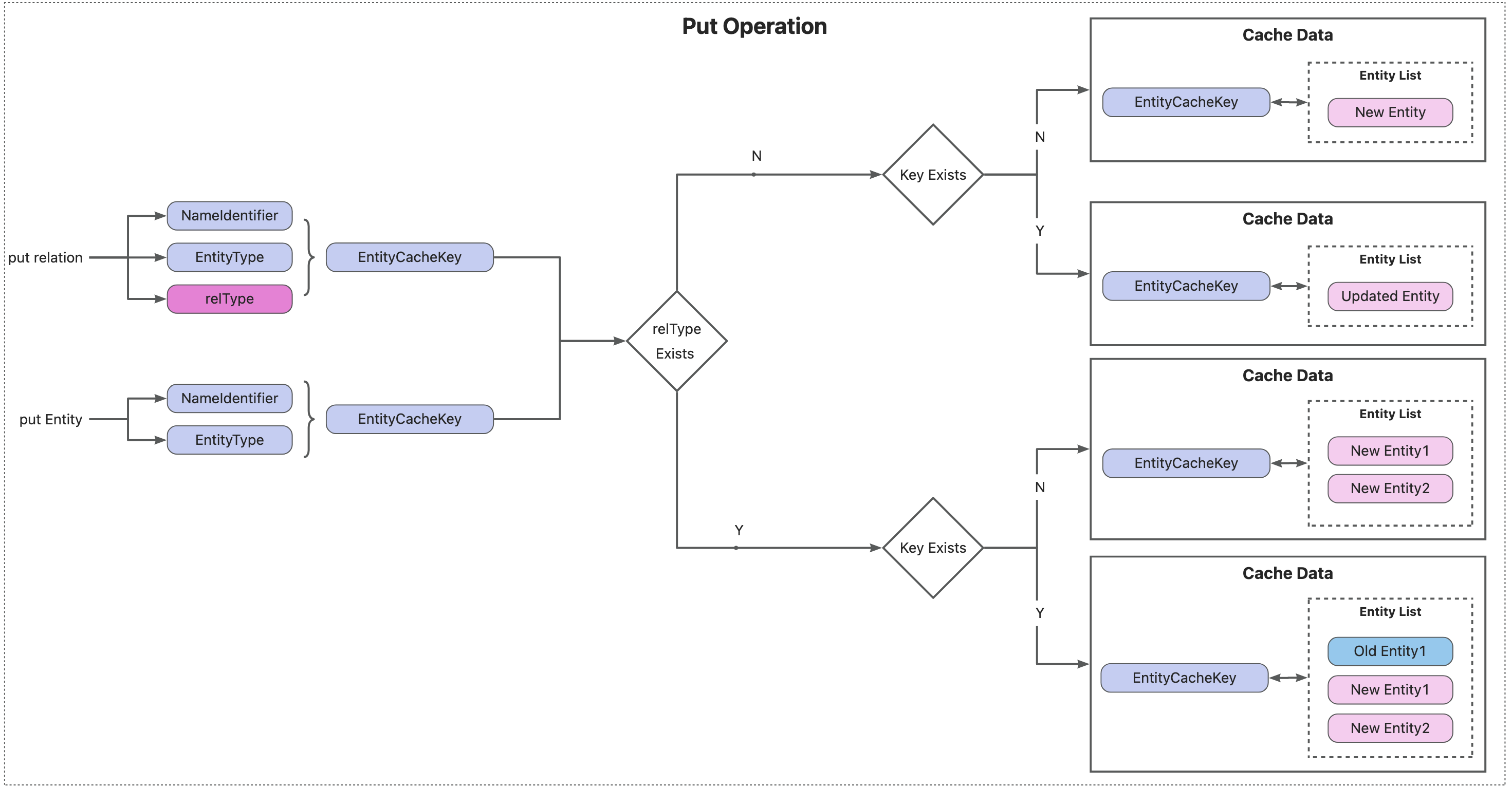
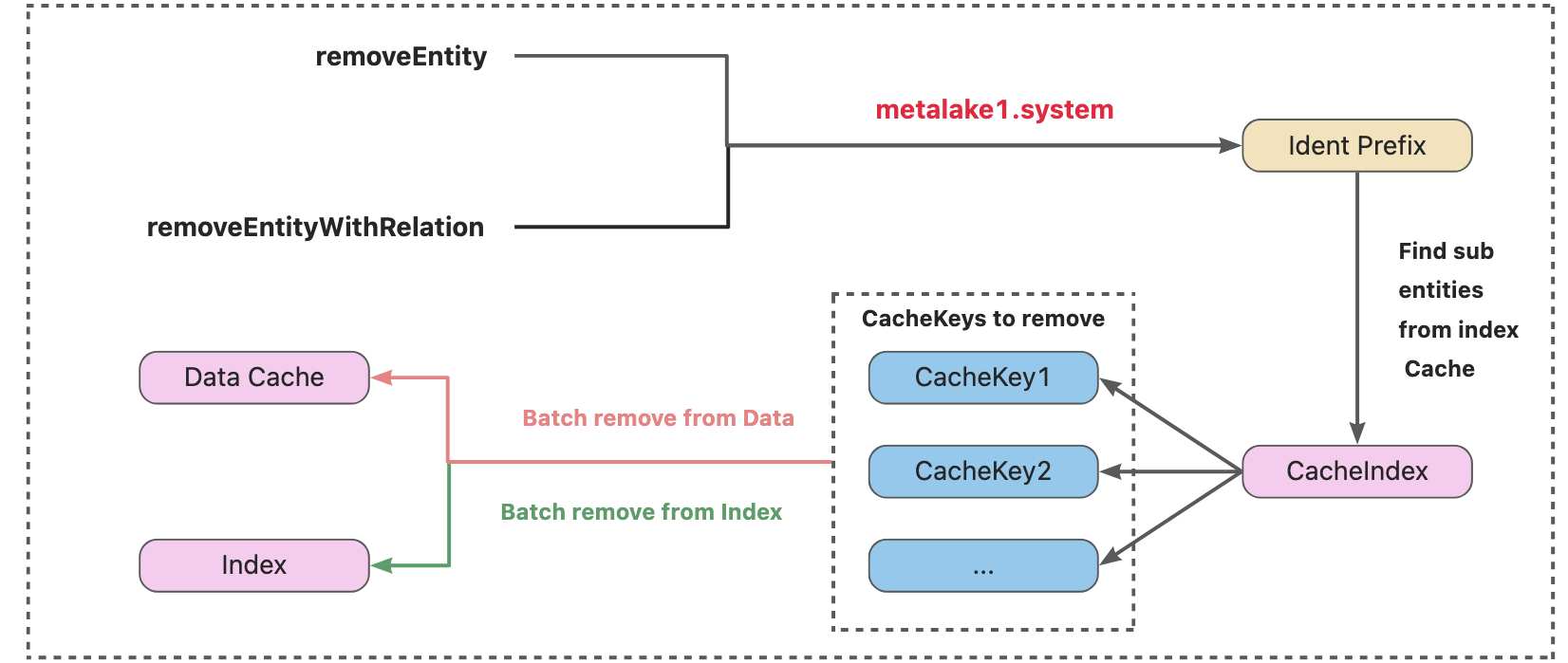
invalidate 操作
首先通过前缀树检索待删除对象的 NameIdentifier 和 ID,再依次删除数据缓存与索引缓存,确保一致性。
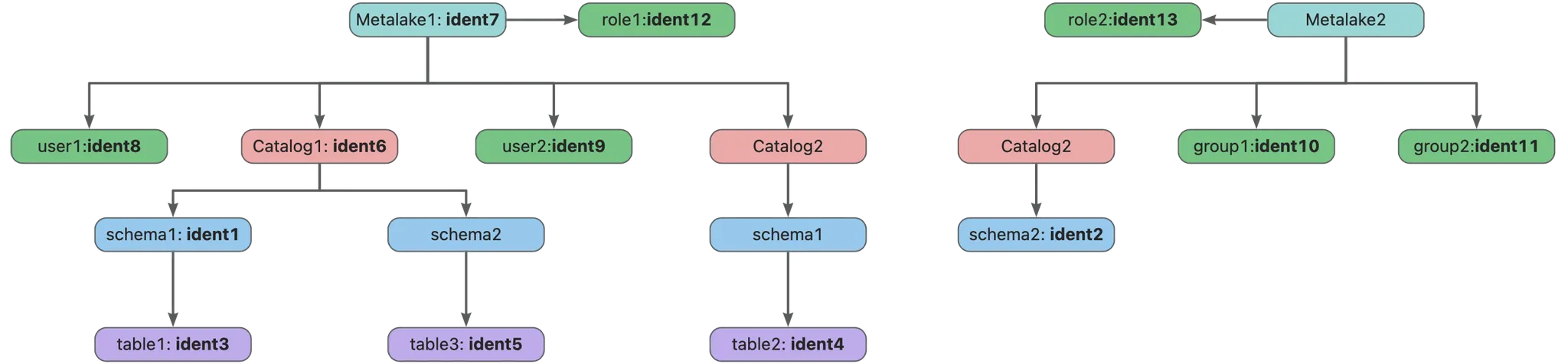
测试
测试使用的 Entity 实体;
UT 测试
| Category | Test Case Description | Method (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Functionality | Basic put/get/getIfPresent operations | testPutAndGet, testGetIfPresent |
| Same identifier with different entity types | testPutSameIdentifierEntities |
|
| Size counting | testSize |
|
| Clear the cache | testClear |
|
| Invalidation | Invalidate by METALAKE/CATALOG/SCHEMA/TABLE level | testInvalidateMetalake, testInvalidateCatalog, testInvalidateSchema, testInvalidateTable |
| Invalidate non-existent entity | testRemoveNonExistentEntity |
|
| Relation Handling | Put/Get/Invalidate entity relations | Covered in multiple tests (e.g., testPutAndGet, testGetIfPresent) |
| Eviction Policies | Expire by time | testExpireByTime |
| Expire by weight | testExpireByWeight |
|
| Exceed max weight immediately | testExpireByWeightExceedMaxWeight |
|
| Expire by size | testExpireBySize |
|
| Weight Logic | Correctness of entity weight calculation | testWeightCalculation |
| Error & Boundary | Null argument checks | testGetIfPresentWithNull, testContainsWithNull, testInvalidateWithNull, testPutWithNull |
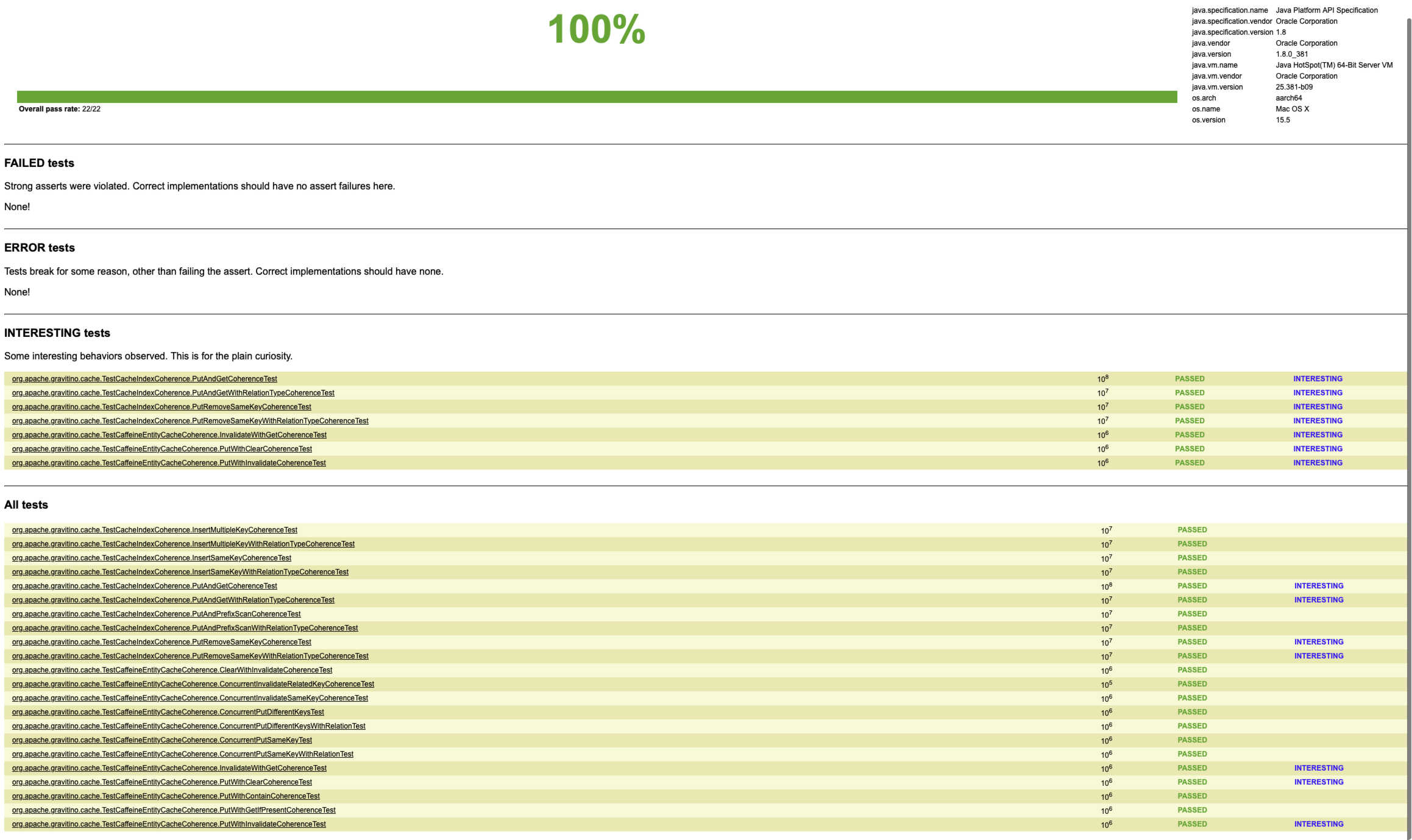
多线程一致性测试
测试采用 JCStress 框架,主要目的是验证 CaffeineEntityCache 在多线程高并发场景下的可见性和一致性。相比传统的单线程或 JUnit-based 多线程测试,JCStress 更适合挖掘在 JMM(Java Memory Model)层级上的竞态问题。
| Test Case | Scenario | Expected Outcome (s) | Unexpected Outcome (s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PutWithGetIfPresentCoherenceTest | put vs getIfPresent | ENTITY | NULL | getIfPresent should always see the entity after put. |
| PutWithContainCoherenceTest | put vs contains | ENTITY | NULL | contains should return true after repeated put. |
| PutWithInvalidateCoherenceTest | put vs invalidate | ENTITY | NULL | Race: either put or invalidate wins, both acceptable. |
| PutWithClearCoherenceTest | put vs clear | ENTITY | NULL | Race: either put or clear wins, both acceptable. |
| ConcurrentPutDifferentKeysTest | concurrent put (different keys) | 2 | 1 or 0 | Both entities should be visible; lower count indicates visibility issue. |
| ConcurrentPutDifferentKeysWithRelationTest | concurrent put (diff rel keys) | 2 | 1 or 0 | Both relation entries should be visible. |
| ConcurrentPutSameKeyTest | concurrent put (same key) | 1 | 0 | Value should remain visible after concurrent put. |
| ConcurrentPutSameKeyWithRelationTest | concurrent put (same key with rel) | 1 | 0 | Relation value should remain visible. |
| InvalidateWithGetCoherenceTest | invalidate vs getIfPresent | ENTITY | NULL | Race: get may or may not see the entity. |
| ConcurrentInvalidateSameKeyCoherenceTest | invalidate x2 (same key) | SUCCESS | FAILURE | Idempotent invalidate should remove key safely. |
| ConcurrentInvalidateRelatedKeyCoherenceTest | invalidate x2 (related keys) | SUCCESS | FAILURE | Both keys should be removed safely. |
| ClearWithInvalidateCoherenceTest | clear vs invalidate | SUCCESS | FAILURE | All keys should be removed; no residue expected. |
测试结果如下:
性能测试
Cache 的性能测试采用 JMH 框架,JMH(Java Microbenchmark Harness)是由 OpenJDK 团队开发的一个基准测试框架,用于构建、运行和分析精确的 Java 微基准测试。它专为测量细粒度操作的性能而设计,例如方法调用、缓存访问或对象分配等,这些操作的性能测量对精度要求极高,毫秒级的精度已无法满足需求。
测试使用的配置如下:
- CPU: Apple M2 Pro
- Memory: 16 GB
- OS: macOS Ventura 15.5
- JVM: openjdk version “17.0.15”
- JMH Version: 1.37
- Benchmark Config:
@BenchmarkMode: Throughput & AverageTime@State: Scope.Thread@Fork: 1@Warmup: 5 iterations@Measurement: 10 iterations
Benchmark (totalCnt) Mode Cnt Score Error Units
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 10 thrpt 10 536704.823 ± 36351.106 ops/s
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 100 thrpt 10 89391.338 ± 4692.738 ops/s
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 1000 thrpt 10 8406.573 ± 738.173 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 10 thrpt 10 19008727.286 ± 1172892.696 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 100 thrpt 10 19129605.626 ± 928728.148 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 1000 thrpt 10 17954917.808 ± 916939.288 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 10 thrpt 10 9454829.072 ± 403482.020 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 100 thrpt 10 5910924.166 ± 234228.471 ops/s
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 1000 thrpt 10 1021172.939 ± 188152.980 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 10 thrpt 10 17646662.661 ± 1850512.796 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 100 thrpt 10 17906401.139 ± 905521.957 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 1000 thrpt 10 17882451.612 ± 1013749.411 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 10 thrpt 10 7949607.041 ± 323537.818 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 100 thrpt 10 4939219.694 ± 54283.320 ops/s
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 1000 thrpt 10 1060788.506 ± 22922.363 ops/s
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 10 thrpt 10 184227.751 ± 6303.043 ops/s
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 100 thrpt 10 19663.536 ± 684.142 ops/s
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 1000 thrpt 10 1651.429 ± 213.587 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 10 thrpt 10 222207.294 ± 10992.713 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 100 thrpt 10 20128.455 ± 434.551 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 1000 thrpt 10 1902.510 ± 75.715 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 10 thrpt 10 335683.335 ± 34641.231 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 100 thrpt 10 26415.590 ± 1511.666 ops/s
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 1000 thrpt 10 2345.904 ± 89.693 ops/s
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 10 thrpt 10 9416189.995 ± 1018247.698 ops/s
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 100 thrpt 10 944383.407 ± 35235.930 ops/s
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 1000 thrpt 10 79938.016 ± 2466.431 ops/s
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁴ s/op
EntityCacheClearBenchmark.benchmarkClear 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻³ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContains 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁶ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁶ s/op
EntityCacheContainsBenchmark.benchmarkContainsWithRelation 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGet 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁷ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁶ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁶ s/op
EntityCacheGetBenchmark.benchmarkGetWithRelations 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁴ s/op
EntityCacheInvalidateBenchmark.benchmarkInvalidate 1000 avgt 10 0.002 ± 0.001 s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁴ s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPut 1000 avgt 10 0.002 ± 0.001 s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁴ s/op
EntityCachePutBenchmark.benchmarkPutWithRelation 1000 avgt 10 0.002 ± 0.001 s/op
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 10 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁶ s/op
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 100 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁵ s/op
EntityCacheSizeBenchmark.entityCacheSize 1000 avgt 10 ≈ 10⁻⁴ s/op操作复杂度总结如下:
| 操作类型 | 时间复杂度 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
contains |
常量时间的键查找 | |
get |
基于键的直接读取操作 | |
getWithRel |
缓存查找为 ,但列表转换过程带来 的线性开销 | |
put |
每条 → 总体 | 不支持批量写入,需遍历插入 条记录 |
putWithRel |
每条关系 → 总体 | 每个关联列表单独写入 |
invalidate |
逐条或按组清除缓存项 | |
clear |
对所有缓存项进行线性遍历清除 | |
size() |
需扫描所有缓存项以精确计算大小 |
尽管 getWithRel() 操作本身通过键查找缓存是 ,但其主要开销在于将缓存中的 List<Entity> 转换为特定类型的 List<E>。
这个转换过程包括:
- 遍历缓存列表中的所有元素;
- 对每个
Entity进行类型校验和强制类型转换为预期的泛型类型E。
因此,该操作的总体时间复杂度为 ,其中 是单个缓存键下关联实体的数量。随着关联实体数量的增加,这一成本也将线性增长。



